
Enlarge / DirectStorage facilitates direct communication between your GPU and speedy modern SSDs, which can reduce game load times and speed up asset streaming.
One of the newer Xbox features that Microsoft has been working to bring to Windows is DirectStorage, a collection of features that allows fast PCI Express-based NVMe SSDs to communicate directly with your GPU. For DirectStorage 1.0, the main benefit was faster load times—up to 40 percent faster, according to Microsoft. This week Microsoft announced that it's readying DirectStorage 1.1 for release later this year, which will allow game assets to be decompressed on the GPU instead of the CPU, speeding up decompression operations and freeing up your processor to do other things.
Normally, compressed game assets are loaded into system memory and decompressed by the CPU before being sent to the GPU. This circuitous route adds to game load times and can contribute to "pop-in" in games with big open worlds—that effect where you see a bland, less-detailed version of an object for a brief instant before more detailed textures and models have time to load in.
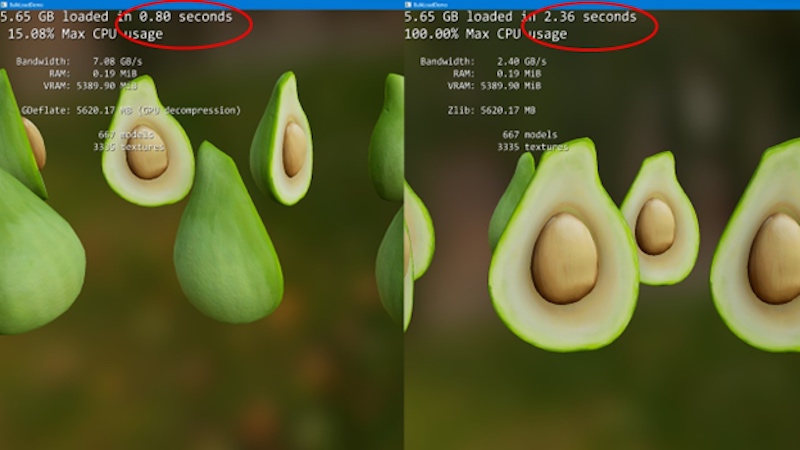
A sample image showing the benefits of GPU-based decompression (left) vs CPU decompression (right). Note the much lower load time and the significantly lowered CPU usage. (credit: Microsoft)
DirectStorage's GPU-based decompression works with a new GPU-optimized compression format called "GDeflate," originally created by Nvidia. Microsoft's sample image comparing GPU decompression with GDeflate and CPU decompression using Zlib showed much faster load times (0.8 second on the GPU, compared to 2.36 seconds on the CPU) along with much lower CPU usage, though Microsoft says that the exact results will vary based on your hardware and the game you're loading.
Read 2 remaining paragraphs | Comments

Enlarge / DirectStorage facilitates direct communication between your GPU and speedy modern SSDs, which can reduce game load times and speed up asset streaming.
One of the newer Xbox features that Microsoft has been working to bring to Windows is DirectStorage, a collection of features that allows fast PCI Express-based NVMe SSDs to communicate directly with your GPU. For DirectStorage 1.0, the main benefit was faster load times—up to 40 percent faster, according to Microsoft. This week Microsoft announced that it's readying DirectStorage 1.1 for release later this year, which will allow game assets to be decompressed on the GPU instead of the CPU, speeding up decompression operations and freeing up your processor to do other things.
Normally, compressed game assets are loaded into system memory and decompressed by the CPU before being sent to the GPU. This circuitous route adds to game load times and can contribute to "pop-in" in games with big open worlds—that effect where you see a bland, less-detailed version of an object for a brief instant before more detailed textures and models have time to load in.

A sample image showing the benefits of GPU-based decompression (left) vs CPU decompression (right). Note the much lower load time and the significantly lowered CPU usage. (credit: Microsoft)
DirectStorage's GPU-based decompression works with a new GPU-optimized compression format called "GDeflate," originally created by Nvidia. Microsoft's sample image comparing GPU decompression with GDeflate and CPU decompression using Zlib showed much faster load times (0.8 second on the GPU, compared to 2.36 seconds on the CPU) along with much lower CPU usage, though Microsoft says that the exact results will vary based on your hardware and the game you're loading.
Read 2 remaining paragraphs | Comments
October 14, 2022 at 09:12PM

Post a Comment