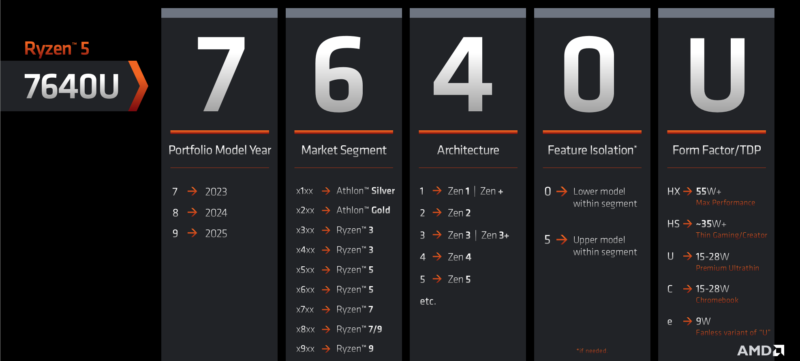
Enlarge / AMD's new naming scheme for Ryzen 7000 laptop CPUs, broken down. (credit: AMD)
Even for someone who pays a lot of attention to them, processor model numbers can be hard to parse. Ideally, each model number would communicate information about the chip's underlying technology and capabilities, making it easy to quickly tell the difference between a new chip and an old chip or a fast chip and a slow chip. But these model numbers also serve a marketing purpose, both for AMD and for PC makers who want to advertise that their systems are using the latest and greatest chips.
AMD is making an effort to resolve this tension with a revamp of its laptop CPU model numbers, which will go into effect in 2023, when Ryzen 7000-branded laptop processors begin shipping. Here's how AMD breaks it down:
- The first digit now indicates the year in which the CPU was launched, with Ryzen 7000 CPUs coming in 2023, Ryzen 8000 in 2024, and Ryzen 9000 in 2025.
- A higher second digit indicates better performance. It will no longer have anything to do with the underlying CPU architecture, as it sometimes does for older chips (Ryzen 5 5500U is Zen 2-based, for example, while Ryzen 5 5600U is Zen 3-based).
- The third digit will now indicate the CPU architecture being used. A "1" means either the original Zen or Zen+, a "2" denotes Zen 2, a "3" denotes either Zen 3 or Zen 3+, a "4" denotes Zen 4, and a "5" will refer to the as-yet-unannounced Zen 5.
- The fourth digit is another loose performance indicator. CPUs ending in "0" will be slower, and CPUs ending in "5" will be faster (as of this writing, those are the only two numbers in use).
- The suffix will denote the TDP of the chip, as it currently does. HX-series chips start at 55 W TDPs, Hs-series chips start at 35 W, U-series chips range from 15 to 28 W, e-series chips are 9 W parts targeted at fanless systems, and C-series chips are just U-series chips in Chromebooks instead of Windows PCs.
AMD also provided this slide, showing how the new model numbers will work in practice for the Ryzen 7000 series (which will encompass at least four distinct CPU architectures, from Zen 2 to Zen 4).
Read 5 remaining paragraphs | Comments

Enlarge / AMD's new naming scheme for Ryzen 7000 laptop CPUs, broken down. (credit: AMD)
Even for someone who pays a lot of attention to them, processor model numbers can be hard to parse. Ideally, each model number would communicate information about the chip's underlying technology and capabilities, making it easy to quickly tell the difference between a new chip and an old chip or a fast chip and a slow chip. But these model numbers also serve a marketing purpose, both for AMD and for PC makers who want to advertise that their systems are using the latest and greatest chips.
AMD is making an effort to resolve this tension with a revamp of its laptop CPU model numbers, which will go into effect in 2023, when Ryzen 7000-branded laptop processors begin shipping. Here's how AMD breaks it down:
- The first digit now indicates the year in which the CPU was launched, with Ryzen 7000 CPUs coming in 2023, Ryzen 8000 in 2024, and Ryzen 9000 in 2025.
- A higher second digit indicates better performance. It will no longer have anything to do with the underlying CPU architecture, as it sometimes does for older chips (Ryzen 5 5500U is Zen 2-based, for example, while Ryzen 5 5600U is Zen 3-based).
- The third digit will now indicate the CPU architecture being used. A "1" means either the original Zen or Zen+, a "2" denotes Zen 2, a "3" denotes either Zen 3 or Zen 3+, a "4" denotes Zen 4, and a "5" will refer to the as-yet-unannounced Zen 5.
- The fourth digit is another loose performance indicator. CPUs ending in "0" will be slower, and CPUs ending in "5" will be faster (as of this writing, those are the only two numbers in use).
- The suffix will denote the TDP of the chip, as it currently does. HX-series chips start at 55 W TDPs, Hs-series chips start at 35 W, U-series chips range from 15 to 28 W, e-series chips are 9 W parts targeted at fanless systems, and C-series chips are just U-series chips in Chromebooks instead of Windows PCs.
AMD also provided this slide, showing how the new model numbers will work in practice for the Ryzen 7000 series (which will encompass at least four distinct CPU architectures, from Zen 2 to Zen 4).
Read 5 remaining paragraphs | Comments
September 07, 2022 at 10:52PM

Post a Comment